반응형

- 카이랄(Chiral): 분자의 거울상과 동일하지 않아 두 개의 거울상 이성질 형태로 존재하는 비대칭성을 일컫는 속성.
- 어떤 분자가 카이랄인지 판단하기 위한 방법: 한 분자가 대칭면을 가지면 카이랄이 아니다.
- 대칭면(plane of symmetry): 어떤 분자의 중심을 통과하여 반으로 자를 때, 분자의 한쪽 반이 정확히 다른 쪽 반의 거울상이 되는 면.
- 비카이랄(nonchiral or achiral): 대칭면을 가져 거울상과 동일한 것.
- 예: propionic acid는 대칭면을 가져 비카이랄인 반면, lactic acid는 대칭면이 없어 카이랄이다.

- 5-1에서 언급한 바와 같이 보통의 유기 분자에서 카이랄성을 일으키는 원인은 탄소 원자에 결합된 네 개의 서로 다른 치환기의 존재다. 이때 카이랄성을 일으키는 중심 탄소 원자를 카이랄성 중심(chirality center)이라 부른다.
- 카이랄성 중심은 분자식에서 *로 표시한다.
- 예: 5-bromodecane

- 카이랄성 중심을 판단하기 위한 간단한 세 가지 규칙
- 모든 -CH3, -CX3 탄소는 카이랄성 중심이 아니다.
- 모든 -CH2-, -CX2- 탄소 카이랄성 중심이 아니다.
- 모든 이중결합, 삼중결합 탄소는 카이랄성 중심이 아니다.
Problem 5-1. Which of the following objects are chiral?
(a) soda can (b) screwdriver (c) screw (d) shoe
Answer.
(d) shoe
Problem 5-2. Which of the following molecules are chiral? Identify the chirality center(s) in each.

Answer.

Problem 5-3. Alanine, an amino acid found in proteins, is chiral. Draw the two enantiomers of alanine using the standard convention of solid, wedged, and dashed lines.
Answer.

Problem 5-4. Identify the chirality centers in the following molecules.
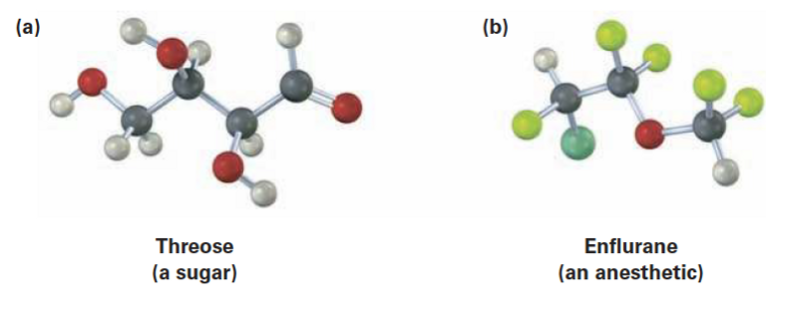
Answer.
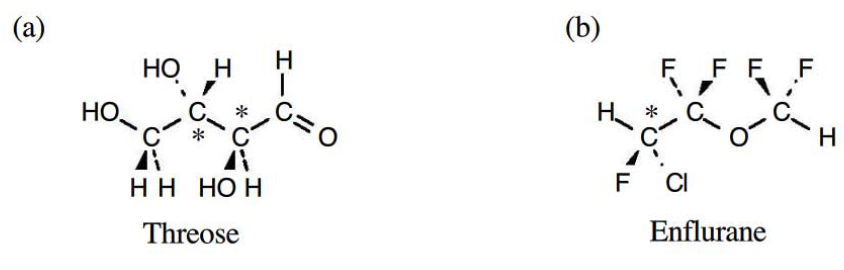
반응형
'전공 지식 > 유기화학 (Organic chemistry)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [유기화학] 5-4. Pasteur의 거울상이성질체 발견 (Pasteur’s discovery of enantiomers) (0) | 2023.02.26 |
|---|---|
| [유기화학] 5-3. 광학 활성 (Optical activity) (0) | 2023.02.25 |
| [유기화학] 5-1. 거울상이성질체와 정사면체 탄소 (Enantiomers and the tetrahedral carbon) (0) | 2023.02.21 |
| [유기화학] 4-9. 여러고리 분자의 형태 (Conformations of polycyclic molecules) (0) | 2023.02.19 |
| [유기화학] 4-8. 이치환 cyclohexane의 형태 (Conformations of disubstituted cyclohexanes) (0) | 2023.02.18 |